

What is the Lithotomy Position?
The lithotomy position, a variant of the supine position, is a common type of patient position that is utilized in various medical examinations and surgical procedures. In this position, the patient is face-up, arms to the sides, but the legs are separated, raised, and supported in a boot-style leg holder or Lithotomy Stirrups.
The position is named for its connection with lithotomy, a procedure to remove bladder stones. While it’s still used for lithotomy procedures, it now has many other uses.
What is the Lithotomy Position Used for?
The lithotomy position is commonly used during gynecologic, rectal, and urologic examinations or surgeries.
The positioning facilitates access to specific anatomical structures, such as the organs of the urinary and reproductive system as well as the rectum and anus. For example, the lithotomy position is the preferred position for childbirth or vaginal ultrasound. Additionally, lithotomy is a common position selected in urethral surgeries, colon surgeries, and removal of bladder stones. The surgical removal of rectal or prostate tumors may also be performed in the lithotomy position.
How Do You Put a Patient in Lithotomy Position?
To successfully place a patient in a lithotomy position, a healthcare provider needs to follow a series of specific steps as defined by their facility's protocol and guidelines.
The patient is placed on their back face-up and the head is supported by a patient positioning pad. The legs are elevated at their hips and the knees are bent at a 70 to a 90-degree angle. The legs are supported in padded footrests like leg stirrups.
Following these steps can help ensure the safety and comfort of the patient during their medical procedure.
Complications Associated With The Lithotomy Position
Like other patient positions, the Lithotomy Position can be associated with a patient increased risk for some strains or injuries, whether used during childbirth or surgery.
Complications during childbirth
● Increased chance of needing an episiotomy which is cutting the tissue between the vagina and anus, also called the perineum
● Increased chance of needing a Caesarian section or forceps
● Increased chance of getting a sphincter injury due to increased pressure
Complications during surgery
● Acute Compartment Syndrome when pressure increases within a specific area of your body
● Nerve Injury: includes two common injuries:
- Peripheral (peroneal) nerve injury increases with the length of surgery. Symptoms include ankle extension, ankle eversion, and foot dorsiflexion.
- Lateral femoral nerve injury which leads to lateral thigh pain or meralgia paresthetica.
- Other common injuries include hip dislocation, tendon and/or muscle strain, low back strain, Sciatic nerve injury, and pressure injuries.
Any surgery carries its own risk of complications. Talk to your doctor about any concerns you have about an upcoming surgery, and don’t feel uncomfortable asking questions about what they’ll do to reduce your risk of complications.
Alternative Positions To The Lithotomy Position During Childbirth
With risk factors associated with Lithotomy Position during childbirth, alternative positions have been adopted and proven to be less risky for women’s health. Some of these alternatives are:
● Kneeling – you can rest by leaning forward between contractions
● Sitting – you can sit astride a chair and lean forward resting on a cushion or pillow, sit on a birthing ball or a beanbag
● Supported standing or squatting
● Lying on the side
Common Variations Of The Lithotomy Position
The Lithotomy Position can take different variations depending on the surgical operation being held.
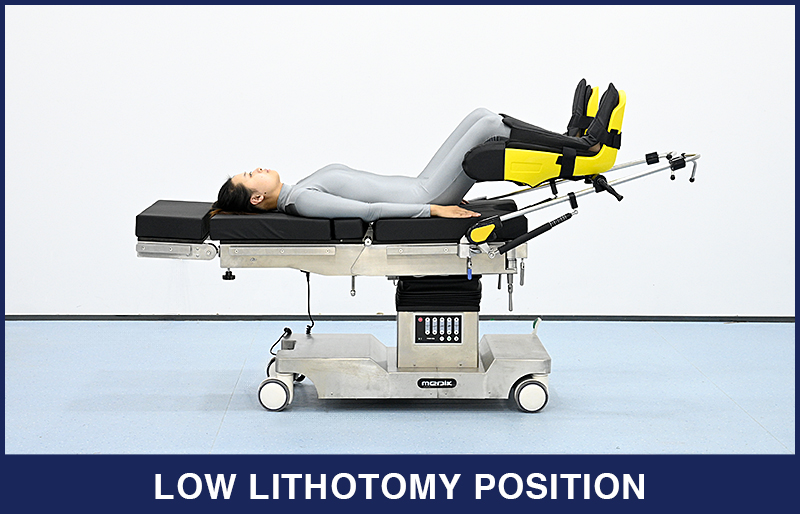
1. Low Lithotomy Position
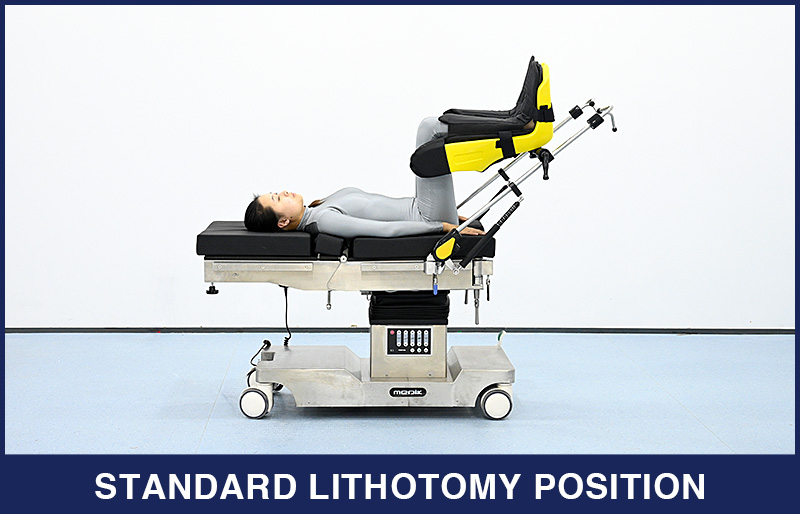
2. Standard Lithotomy Position
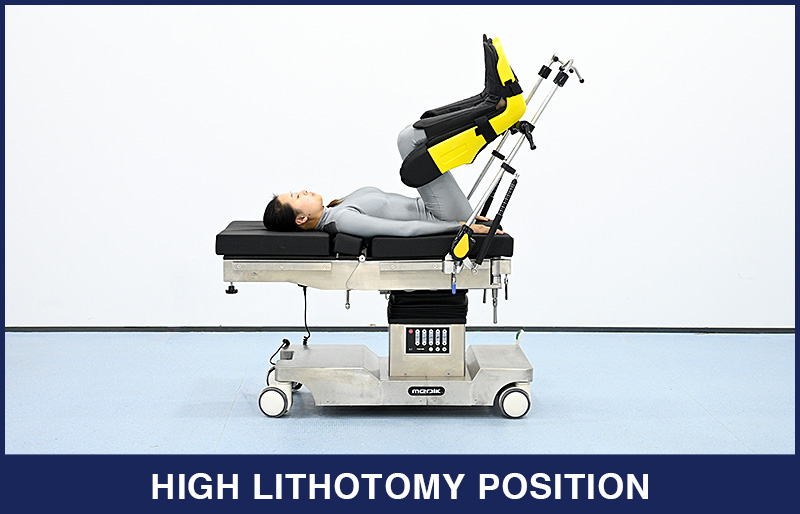
3. High Lithotomy Position
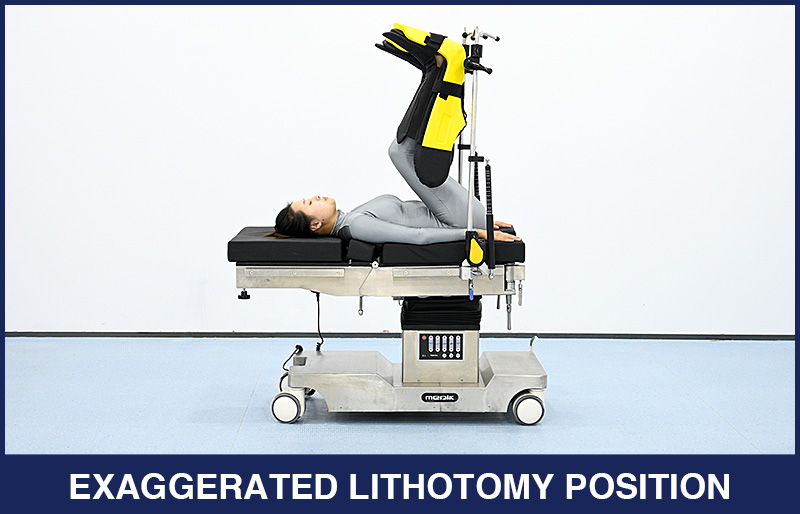
4. Exaggerated Lithotomy Position
5. Hemi (split) Lithotomy Position
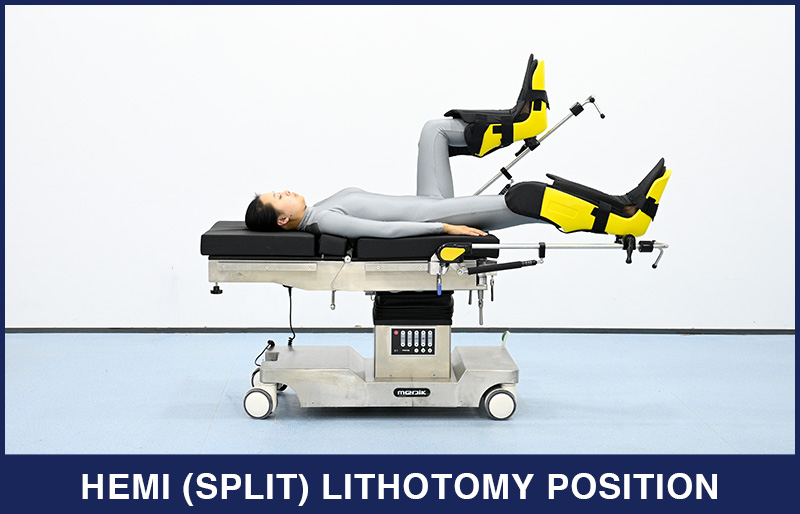
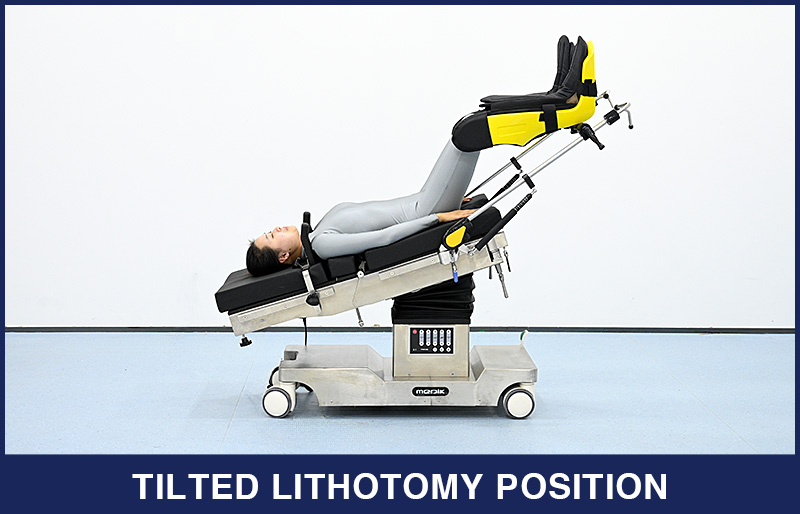
6. Tilted Lithotomy Position (Trendelenburg Position)
Conclusion
The lithotomy position is a medical posture where a patient lies on their back with legs raised and supported, commonly used in gynecological, rectal, and urological procedures. It provides easy access to the pelvic organs, making it the preferred choice for childbirth, vaginal ultrasounds, and certain surgeries. It carries certain risks that can make it potentially dangerous in some situations. To minimize complications, other positions may be considered as safer alternatives.
Related Resources
Resources for research and reference
1.Karkenny AJ, Mendelis JR, Geller DS, Gomez JA. The role of intraoperative navigation in orthopaedic surgery. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019;27(19):e849-e858. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-18-00478
2.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4877173/
3. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4600206/
4.Kuponiyi O, et al. (2014). Nerve injuries associated with gynecological surgery.
DOI: 10.1111/tog.12064
5.https://www.nhsinform.scot/ready-steady-baby/labour-and-birth/labour/labour-positions/