

From sanitation to lighting, the environment in which your surgical team operates has a lot to do with the success of the procedure. The market is filled with various kinds of surgical lights, and each kind of surgical light serves a particular purpose in illuminating a medical procedure before, during, and after it. It can be not easy to know which is best for your hospital, surgical center, or dentist’s office. The good news is that, once you understand the main types of surgical lighting, you can make a more informed choice of product.
Today we'll dig into them and look at the different types of surgical lights. They can be classified by positioning, source, or mounting configuration.
Types of Surgical Lights: Positioning
There are three main types of surgical lighting for the position: overhead, headlights, and in-cavity lighting. Each has unique advantages and is suitable for various settings.
Overhead Lighting
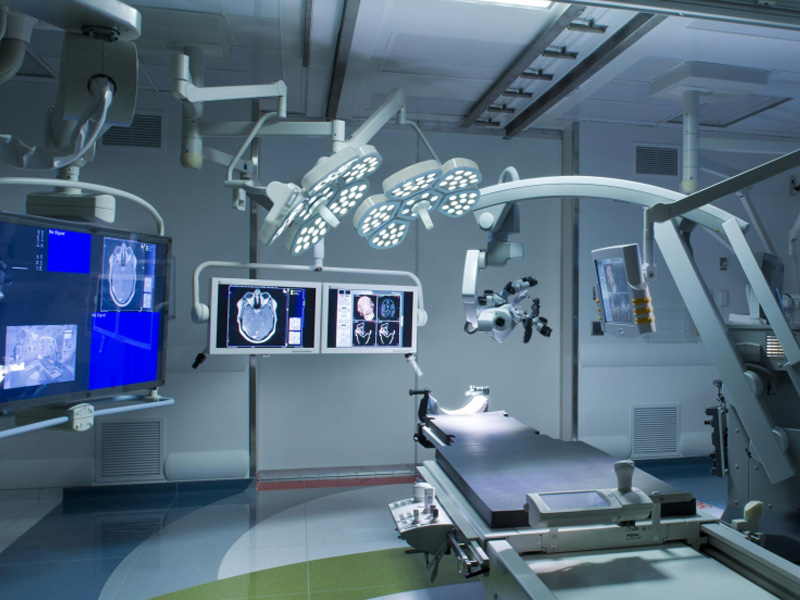
Overhead lights are the most recognized surgical lights. Overhead lighting is suspended from a mount attached to the ceiling or wall. It is easily adjustable to flood operating areas with light.
Surgeons manipulate the lights by grabbing the removable handles that can be sterilized after a procedure.
The overhead lights are perfect for lighting the general field and for relatively shallow open surgeries however it does not offer the directed light needed for deep cavities and detailed illumination and is still subject to shadowing due to objects between the light and the field. In addition, they can create a diffused light pattern which can affect the surgeon’s view of the surgical site. Likewise,and it puts off a lot of heat, which can be problematic in certain situations.When considering new OT lights, it is important to take into account factors such as shadow and heat generation.
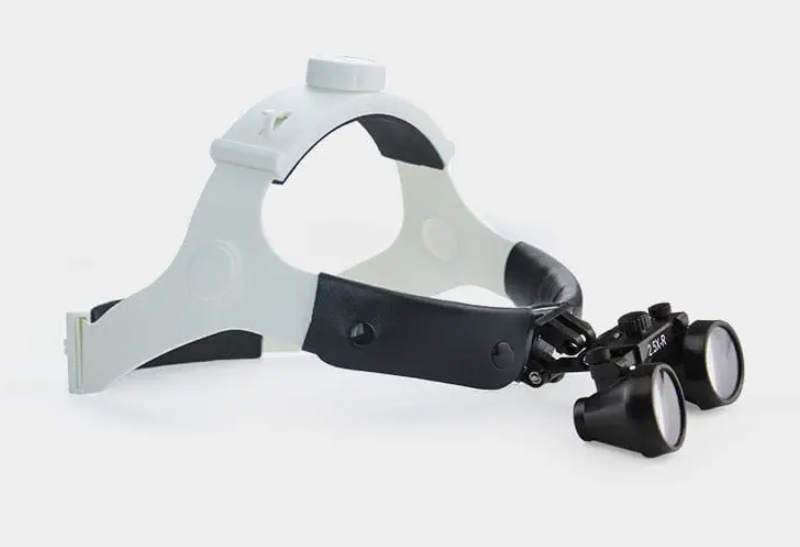
Surgical Headlight
Headlamps are wearable devices that provide great precision and a hands-free method for illuminating the surgical area. They naturally follow the directions in which the surgeon is looking. These headlamps can be powered by batteries or connected to a separate light source through a fiber optic cable.
Headlamps also can incorporate “surgical loupes.” These are magnifying glasses that enlarge and/or enhance the clarity of the surgical site.

In-Cavity Lighting
In-cavity lighting is only used in very specific circumstances. These usually involve situations where other types of lighting are inadequate. It entails a lamp that attaches to a retractable wand or another instrument.
This type of lighting is ideal for deeper cavities or areas with angles that are difficult to illuminate with standard medical equipment. One challenge is ensuring heat management when using this type of lighting.
Types of Surgical Lights: Source
There are many different types of bulbs used in surgical lighting. The two most prominent are halogen and LED lights.
Halogen surgical light
Halogen lighting, similar to regular incandescent bulbs, has been a common choice in surgical settings for many years due to its reliability and low cost. It also offers easy disposal.One difference from incandescent is that halogen bulbs use a tungsten filament that mixes with halogen gas. This combination triggers a chemical process that deposits vaporized tungsten back onto the filament. The filament can work at higher temperatures as a result, producing light with greater efficacy and color temperature.
A drawback of halogen bulbs is that they put off a great deal of infrared light, which needs to be filtered to create a cooler white light suitable for surgery. Additionally, they generate substantial heat, which must be managed to keep your surgical team from becoming too hot.
Halogen bulbs are also less efficient than incandescents and LEDs, and will not last as long. Depending on usage, you can expect to replace them about once a year.
LED lights, or “light-emitting diodes,” have become the gold standard in surgical lights. They work by passing an electric current through a semiconducting material (the diode).
This process of producing light does not create heat. This makes LEDs highly suitable for surgical procedures as they keep the surgical team cool even under direct illumination. They are known for their efficient energy usage, requiring significantly less energy than halogen bulbs to produce higher-quality illumination.
Unlike halogen bulbs that abruptly fail, LEDs gradually fade in brightness over time, making it easier to anticipate when replacement is needed. It also can help avoid situations where surgery lighting abruptly fails.
Upfront costs are one drawback to LED lights. However, when you factor in their longevity, as well as their energy efficiency, the price difference may be negligible. Also, with advances in technology, LED light prices continue to decrease.
Types of Surgical Lights: Mounting Configuration
Surgical lighting configurations can be ceiling-mounted, wall-mounted, or floor-standing. The best light configuration for your practice will be largely dependent on the type of illumination your procedure or examination requires.
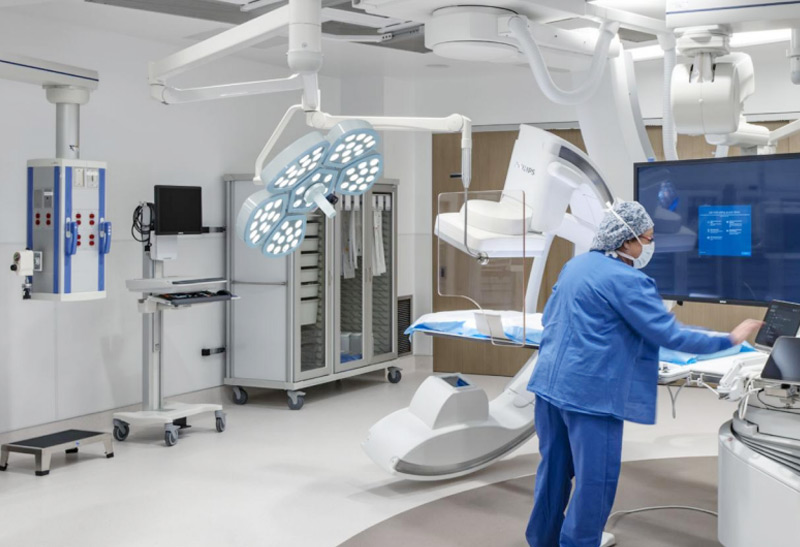
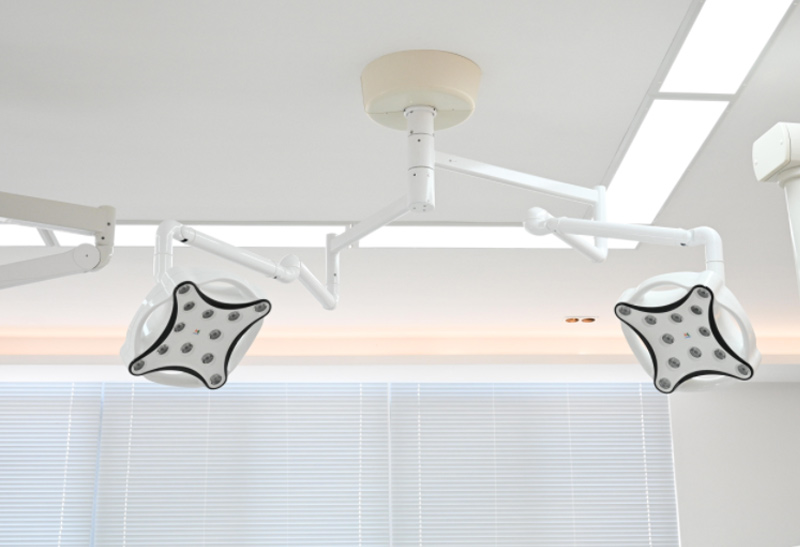
Ceiling-mounted Surgical Lights
Ceiling-mounted surgical lights are fixtures installed on the ceiling of the operating room. These lights provide a wide, even beam of light that illuminates the entire surgical field. They efficiently provide illumination at the surgical site, ensure high-quality signals for imaging, reduce energy consumption by one-third, and eliminate the need for bulb replacements.

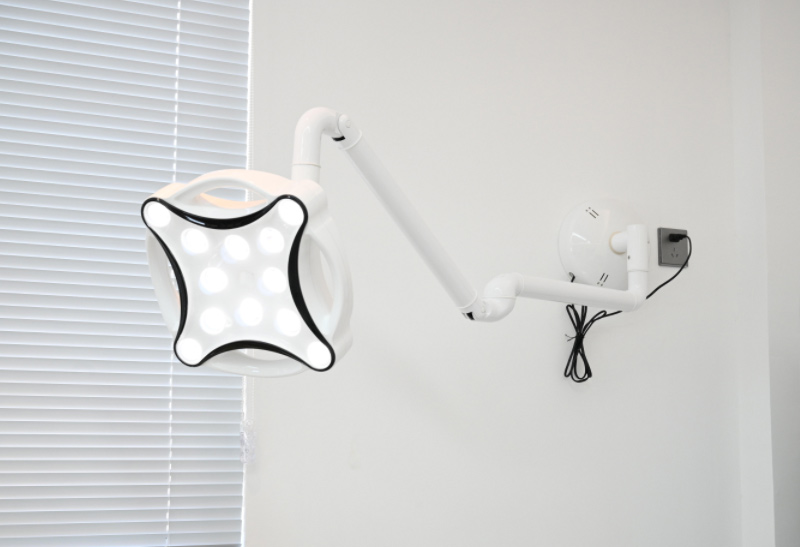
Wall-mounted Exam Lights
Wall-mounted lights are positioned on the OR wall. These lights are a space-saving option for small rooms. This type of lighting is more frequently employed with medical examination lights rather than surgical lights.

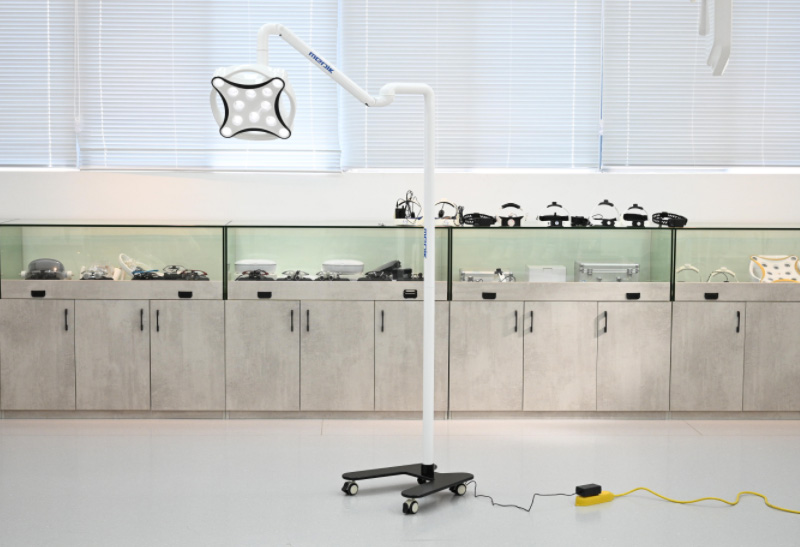
Floor-standing Surgical Lights
Floor-standing surgical lights are a versatile and flexible option for surgical lighting. They are typically used in conjunction with ceiling-mounted surgical lights, but they can also be used as a primary light source. Floor-standing surgical lights are portable, which makes them easy to move around the operating room. These lights are also employed in medical examinations.

Final Thought
Now that you know about the different types of surgical lighting and the benefits of each, you can decide which is best for your practice. Remember the right setup and bulb type depends on your unique surgery requirements. Learning as much as you can about the advantages of each can lead to more successful surgical and better health outcomes.
Medik offers a complete line of surgical lights medical exam lights and headlights. Call us today at +86 13962231292 or email us at info@mediksurgical.com